What is it about?
Type A Carbohydrate-Binding Modules (CBMs) are a critical component of cellulose-degrading microbial enzymes, but their mechanism of action remains poorly understood. A library of recombinant type A CBMs in fusion with green fluorescent protein was constructed and their binding to cellulose and chitin was characterized over a wide range of temperatures, pHs and ionic strengths. The structure of S. thermophila StCBM64C was further solved, revealing an untwisted, flat, carbohydrate-binding interface comprising the side chains of four tryptophan residues in a coplanar linear arrangement.
Featured Image
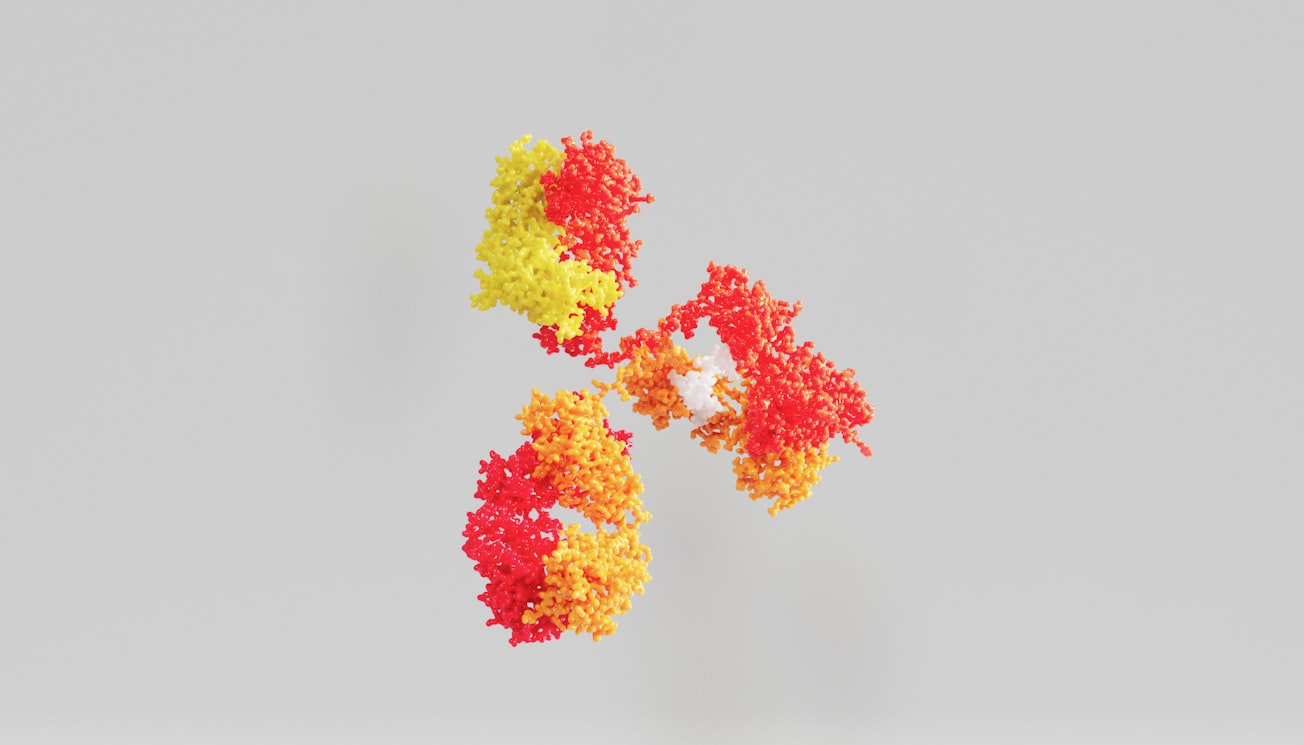
Photo by ANIRUDH on Unsplash
Read the Original
This page is a summary of: Stability and ligand promiscuity of type A carbohydrate-binding modules are illustrated by the structure of Spirochaeta thermophila StCBM64C, Journal of Biological Chemistry, February 2017, American Society for Biochemistry & Molecular Biology (ASBMB),
DOI: 10.1074/jbc.m116.767541.
You can read the full text:
Resources
Binding of a carbohydrate binding module fused to green fluorescent protein to cellulose microparticles
Fluorescence microscopy photography of carbohydrate binding module-green fluorescent protein (CBM3-GFP) fusions bound to cellulose 20 micron-sized microparticles. The CBM3 is from C. thermocellum.
Binding of a carbohydrate binding module from Pyrococcus furiosus to chytosan microparticles
Fluorescence microscopy photography of a fusion of a carbohydrate binding module from Pyrococcus furiosus with green fluorescent protein (GFP-CBM2) bound to low molecular weight chytosan micron-sized microparticles. Images were taken with a Leica DMLB fluorescence microscope (20x magnification).
Binding of a carbohydrate binding module from Pyrococcus furiosus to microcrystalline cellulose
Fluorescence microscopy photography of a fusion of a carbohydrate binding module from Pyrococcus furiosus with green fluorescent protein (GFP-CBM2) bound to microcrystalline cellulose microparticles. Images were taken with a Leica DMLB fluorescence microscope (20x magnification).
Structure of the Carbohydrate Binding Module 64 from Spirochaeta thermophila
Structure of the carbohydrate binding module 64 from Spirochaeta thermophila. In the structure shown in the video, two beta-sheets are highlighted in yellow and a small helix in red. Four co-planar tryptophan residues (W31, W38, W54 and W78) linearly aligned at the surface of beta-sheet 2 are shown in blue. These residues may constitute the binding site of the flat carbohydrate interacting platform. Molecular graphics performed with the Pymol package.
Biorecognition as a tool for the functionalization of cellulose
A brief overview of my research on the use of carbohydrate binding modules as a tool for the functionalization of cellulose-based materials.
Contributors
The following have contributed to this page







